NeoVim IDE
备注
从零开始配置 Neovim(Nvim) 和 Transform Your Neovim into a IDE: A Step-by-Step Guide 是双语写作的博客,原文作者撰写清晰,推荐阅读。
我参考该文的最新版本再次 重新配置NeoVim IDE
Transform Your Neovim into a IDE: A Step-by-Step Guide 作者提供的指南(借鉴):
从0开始构建基于 Lua 的
nvim配置,努力理解每个配置选项学习一些 Lua 编程语言,可以参考一下 Learn Lua in Y minutes (这个 Learn X in Y minutes 比较有意思,通过案例让你快速入门一门语言)
配置文件路径
先构建配置文件初始化
nvim 的配置路径mkdir -p ~/.config/nvim
mkdir ~/.config/nvim/lua
touch ~/.config/nvim/init.lua
上述创建了一个空的 ~/.config/nvim/init.lua ,这样进入 nvim 之后执行 checkhealth 至少能够看到 Configuration 是OK状态;每次修改 init.lua 都需要重启 nvim 才能看到修改的变化
配置选项
以下配置
~/.config/nvim/lua/options.lua实现了功能:使用系统剪贴板
在
nvim中使用鼠标Tab和空格键
UI配置
灵活搜索
~/.config/nvim/lua/options.lua-- Hint: 如果需要,使用 `:h <option>` 来查找配置含义
vim.opt.clipboard = 'unnamedplus' -- 使用系统剪贴板
vim.opt.completeopt = {'menu', 'menuone', 'noselect'}
vim.opt.mouse = 'r' -- 允许在Nvim中使用鼠标,原文使用 'a' ,不过这样只能在vim内部使用,退出vim就丢失
-- 我修改为 'r' 这样退出vim依然保留剪贴板内容;如果 'r' 无效,则可以尝试 'v' ,实际取决于 vimrc
-- 参考 https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/139578/copy-paste-for-vim-is-not-working-when-mouse-set-mouse-a-is-on
-- Tab
vim.opt.tabstop = 4 -- 每个Tab代表的虚拟空格数量
vim.opt.softtabstop = 4 -- 当编辑时空间tab(spacesin tab)代表的空格数量
vim.opt.shiftwidth = 4 -- 在一个tab中插入4个空格
vim.opt.expandtab = true -- 将tabs转换为空格,这在python有用
-- UI config
vim.opt.number = true -- 显示绝对数值(也就是行号)
vim.opt.relativenumber = true -- 在左边显示没一行的行号
vim.opt.cursorline = true -- 高亮光标水平行下方显示横线
vim.opt.splitbelow = true -- 打开新的垂直分割底部
vim.opt.splitright = true -- 在水平分割右方打开
-- vim.opt.termguicolors = true -- 在TUI激活24位RGB颜色
vim.opt.showmode = false -- 根据经验,我们不需要 "-- INSERT --" 模式提示
-- Searching
vim.opt.incsearch = true -- 在输入字符时搜索
vim.opt.hlsearch = false -- 不要高亮匹配项
vim.opt.ignorecase = true -- 默认搜索时不区分大小写
vim.opt.smartcase = true -- 如果搜索时输入一个大写字母则表示搜索区分大小写
在
init.lua中添加以下配置激活使用options.lua:
~/.config/nvim/init.lua 中激活 options.luarequire('options')
require('keymaps')
require('plugins')
require('colorscheme')
require('lsp')
现在显示的效果:
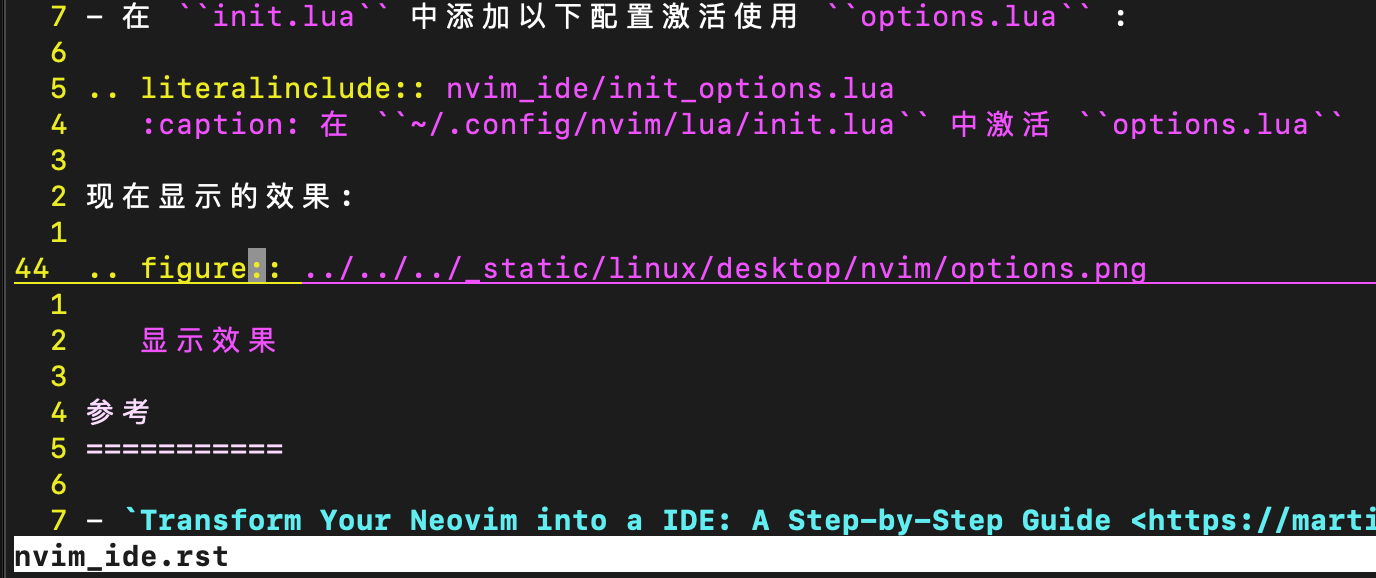
显示效果
键盘映射配置
以下配置
~/.config/nvim/lua/keymaps.lua实现如下键盘映射:使用
<C-h/j/k/l>在窗口间移动光标使用
Ctrl + 方向键来调整窗口大小在select选择模式,可以使用
Tab或者Shift-Tab来更改连续缩排(indentation repeatedly)
~/.config/nvim/lua/keymaps.lua-- 定义常用选项
local opts = {
noremap = true, -- 非递归
silent = true, -- 不显示消息
}
---------------------------
-- 常规模式(Normal mode) --
---------------------------
-- 提示: 查看 `:h vim.map.set()`
-- 最佳窗口导航
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-h>', '<C-w>h', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-j>', '<C-w>j', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-k>', '<C-w>k', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-l>', '<C-w>l', opts)
-- 通过箭头调整窗口大小
-- 变量: 2 行
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-Up>', ':resize -2<CR>', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-Down>', ':resize +2<CR>', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-Left>', ':vertical resize -2<CR>', opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-Right>', ':vertical resize +2<CR>', opts)
---------------------------
-- 可视模式(Visual mode) --
---------------------------
-- 提示: 以之前区域和相同模式启动相同区域的可视模式
vim.keymap.set('v', '<', '<gv', opts)
vim.keymap.set('v', '>', '>gv', opts)
同样在
init.lua中添加以下配置激活使用keymaps.lua:
~/.config/nvim/init.lua 中激活 keymaps.luarequire('options')
require('keymaps')
require('plugins')
require('colorscheme')
require('lsp')
安装包管理器
nvim 通过第三方插件提供了强大的能力。有多种插件管理器,其中 lazy.nvim 非常受欢迎,提供了很多神奇功能:
修正依赖顺序
锁文件
lazy-lock.json跟踪安装的插件...
创建
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua:
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua 管理插件local lazypath = vim.fn.stdpath("data") .. "/lazy/lazy.nvim"
if not (vim.uv or vim.loop).fs_stat(lazypath) then
vim.fn.system({
"git",
"clone",
"--filter=blob:none",
"https://github.com/folke/lazy.nvim.git",
"--branch=stable", -- latest stable release
lazypath,
})
end
vim.opt.rtp:prepend(lazypath)
require("lazy").setup({})
同样在
init.lua中添加以下配置激活使用plugins.lua:
~/.config/nvim/init.lua 中激活 plugins.luarequire('options')
require('keymaps')
require('plugins')
require('colorscheme')
require('lsp')
这里我遇到一个报错:
nvim 版本低于 0.8.0 导致不能使用 lazy.nvim 报错Error detected while processing /home/admin/.config/nvim/init.lua:
lazy.nvim require Neovim >= 0.8.0
解决方法是 Debian环境编译neovim ,安装自己编译的最新版本后,重新执行上述安装包管理器
如果一切正常,首次重新启动 nvim 会有短暂的黑屏(没有输出内容),之后正常见到Dashboard。此时,输入 :Lazy 检查是否工作正常。
配色(Colorscheme)
备注
Monokai Pro 开发的 Monokai color scheme 是开发IDE中最流行的语法高亮配色,在 THE HISTORY OF Monokai 一文中有详细的介绍:
2006年荷兰设计师兼开发者Wimer Hazenberg开发出最初的Monokai,主要是TextMate on macOS上暗黑背景的活泼色彩
随后被各个主要IDE所接纳,并且用于终端色彩
2017年发布了Monokai Pro,进一步采用了现代色彩系列,并且包含了用户接口设计和定制图标,提供了色彩过滤器,例如
Spectrum,Ristretto和Monokai Classic2024年发布了Monokai Pro Light,采用了新的
Sunfilter,适配了明亮环境,也就是说经过多年发展,Monokai已经完成了主流的 dark 和 light 两种环境适配
在完成了上文 lazy.nvim 配置之后,就可以安装配色插件,这里参考原文使用了 monokai.nvim 插件,并且选择了我对比之后认为较为美观的 monokai 风格:
修订
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua,增加安装monokai.nvim的配置行:
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua 增加 monokai.nvim 插件管理配色local lazypath = vim.fn.stdpath("data") .. "/lazy/lazy.nvim"
if not (vim.uv or vim.loop).fs_stat(lazypath) then
vim.fn.system({
"git",
"clone",
"--filter=blob:none",
"https://github.com/folke/lazy.nvim.git",
"--branch=stable", -- latest stable release
lazypath,
})
end
vim.opt.rtp:prepend(lazypath)
require("lazy").setup({
"tanvirtin/monokai.nvim",
})
创建一个
~/.config/nvim/lua/colorscheme.lua来定制monokai.nvim插件:
~/.config/nvim/lua/colorscheme.lua 定制 monokai.nvim 插件-- define your colorscheme here
local colorscheme = 'monokai'
-- local colorscheme = 'monokai_pro'
-- local colorscheme = 'monokai_soda'
-- local colorscheme = 'monokai_ristretto'
local is_ok, _ = pcall(vim.cmd, "colorscheme " .. colorscheme)
if not is_ok then
vim.notify('colorscheme ' .. colorscheme .. ' not found!')
return
end
最后在
~/.config/nvim/init.lua激活配置
~/.config/nvim/lua/init.lua 中激活 colorscheme.luarequire('options')
require('keymaps')
require('plugins')
require('colorscheme')
require('lsp')
自动代码补全(Auto-completion)
nvim 可以配置成自动代码补全,通过一些极佳的插件可以轻易实现。
使用插件 nvim-cmp 可以管理多种自动代码补全功能,也提供了自定义补全菜单等功能。
创建
~/.config/nvim/lua/config/nvim-cmp.lua为nvim-cmp准备配置:
~/.config/nvim/lua/config/nvim-cmp.lua 增加 nvim-cmplocal has_words_before = function()
unpack = unpack or table.unpack
local line, col = unpack(vim.api.nvim_win_get_cursor(0))
return col ~= 0 and vim.api.nvim_buf_get_lines(0, line - 1, line, true)[1]:sub(col, col):match("%s") == nil
end
local luasnip = require("luasnip")
local cmp = require("cmp")
cmp.setup({
snippet = {
-- REQUIRED - you must specify a snippet engine
expand = function(args)
require('luasnip').lsp_expand(args.body) -- For `luasnip` users.
end,
},
mapping = cmp.mapping.preset.insert({
-- Use <C-b/f> to scroll the docs
['<C-b>'] = cmp.mapping.scroll_docs( -4),
['<C-f>'] = cmp.mapping.scroll_docs(4),
-- Use <C-k/j> to switch in items
['<C-k>'] = cmp.mapping.select_prev_item(),
['<C-j>'] = cmp.mapping.select_next_item(),
-- Use <CR>(Enter) to confirm selection
-- Accept currently selected item. Set `select` to `false` to only confirm explicitly selected items.
['<CR>'] = cmp.mapping.confirm({ select = true }),
-- A super tab
-- sourc: https://github.com/hrsh7th/nvim-cmp/wiki/Example-mappings#luasnip
["<Tab>"] = cmp.mapping(function(fallback)
-- Hint: if the completion menu is visible select next one
if cmp.visible() then
cmp.select_next_item()
elseif has_words_before() then
cmp.complete()
else
fallback()
end
end, { "i", "s" }), -- i - insert mode; s - select mode
["<S-Tab>"] = cmp.mapping(function(fallback)
if cmp.visible() then
cmp.select_prev_item()
elseif luasnip.jumpable( -1) then
luasnip.jump( -1)
else
fallback()
end
end, { "i", "s" }),
}),
-- Let's configure the item's appearance
-- source: https://github.com/hrsh7th/nvim-cmp/wiki/Menu-Appearance
formatting = {
-- Set order from left to right
-- kind: single letter indicating the type of completion
-- abbr: abbreviation of "word"; when not empty it is used in the menu instead of "word"
-- menu: extra text for the popup menu, displayed after "word" or "abbr"
fields = { 'abbr', 'menu' },
-- customize the appearance of the completion menu
format = function(entry, vim_item)
vim_item.menu = ({
nvim_lsp = '[Lsp]',
luasnip = '[Luasnip]',
buffer = '[File]',
path = '[Path]',
})[entry.source.name]
return vim_item
end,
},
-- Set source precedence
sources = cmp.config.sources({
{ name = 'nvim_lsp' }, -- For nvim-lsp
{ name = 'luasnip' }, -- For luasnip user
{ name = 'buffer' }, -- For buffer word completion
{ name = 'path' }, -- For path completion
})
})
修订
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua添加:
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua 增加 nvim-cmp 设置...
require("lazy").setup({
-- Vscode-like pictograms
{
"onsails/lspkind.nvim",
event = { "VimEnter" },
},
-- Auto-completion engine
{
"hrsh7th/nvim-cmp",
dependencies = {
"lspkind.nvim",
"hrsh7th/cmp-nvim-lsp", -- lsp auto-completion
"hrsh7th/cmp-buffer", -- buffer auto-completion
"hrsh7th/cmp-path", -- path auto-completion
"hrsh7th/cmp-cmdline", -- cmdline auto-completion
},
config = function()
require("config.nvim-cmp")
end,
},
-- Code snippet engine
{
"L3MON4D3/LuaSnip",
version = "v2.*",
},
...
})
解析:
cmp.setup功能接受一个Lua表,该表定义了一些定制选项。
LuaSnip是一个代码片段引擎(code snippet engine),nvim-cmp可以从该引擎中获取一个代码片段,不过如果你不需要的话可以忽略在
lazy.nvim中的config = function() ... end设置了该插件将要加载的代码,这部分保存在nvim-cmp.lua中
nvim-cmp是主要的插件,其他以cmp-开头的插件是nvim-cmp所使用的自动补全源代码帮手。而lspkind.nvim将这些代码补全显示得更为美观
nvim-cmp 的键盘映射
mapping = ... 语法是 ['<key-binding>'] = cmp.mapping.xxx, ,不同的 cmp.mapping.xxx 选项可以在手册中找到,如果需要修改键盘绑定,只需要修改 [...] ,这里采用:
<C-k/j>或者/来在补全项之间移动
<C-b/f>在补全项的文档中滚动
<CR>确认补全
nvim-cmp 补全菜单
使用 formatting = ... :
fields设置每个补全项目的显示
format = function(...)设置每个补全源代码的文本,你可以在sources = ...设置补全代码的源。
备注
到这里基本配置已经完成
LSP
要将 Nvim 作为IDE,需要依赖LSP实现。但是手动安装和配置LSP很麻烦,因为不同的LSP有不同的安装步骤,对后期的管理来说很不方便。所以就有了 mason.nvim 和 mason-ispconfig.nvim 来简化配置。
修改
plugins.lua添加如下行:
~/.config/nvim/lua/plugins.lua 增加 nason.nvim 相关设置...
require("lazy").setup({
...
-- LSP manager
"williamboman/mason.nvim",
"williamboman/mason-lspconfig.nvim",
"neovim/nvim-lspconfig",
...
})
然后再创建一个
~/.config/nvim/lua/lsp.lua管理mason,这里首先配置mason和mason-ispconfig:
~/.config/nvim/lua/lsp.lua 管理 mason 配置require('mason').setup({
ui = {
icons = {
package_installed = "✓",
package_pending = "➜",
package_uninstalled = "✗"
}
}
})
require('mason-lspconfig').setup({
-- A list of servers to automatically install if they're not already installed
ensure_installed = { 'pylsp', 'lua_ls', 'rust_analyzer' },
})
备注
所有需要添加的LSP都在 ensure_installed 中列出,完整列表见 nvim-lspconfig/doc/server_configurations.md
在上述 lsp.lua 中,不仅需要配置 mason-lspconfig ,之后还需要配置 nvim-lspconfig ,但是这个代码非常长, Transform Your Neovim into a IDE: A Step-by-Step Guide 原文作者给出了一个案例 GitHub:MartinLwx dotfiles/nvim/lua/lsp.lua 来展示 pylsp ,其他配置需要自己根据 nvim-lspconfig/doc/server_configurations.md 来完成。
备注
每个LSP可能需要配置自己的选项,需要检查相应的GitHub仓库啊获得进一步信息,或者仅仅设置 on_attach = on_attach
在
~/.config/nvim/lua/lsp.lua文件中添加如下代码(这里我按照 原文作者给出了一个案例 GitHub:MartinLwx dotfiles/nvim/lua/lsp.lua ):
~/.config/nvim/lua/lsp.lua 添加详细配置-- Note: The order matters: mason -> mason-lspconfig -> lspconfig
require("mason").setup({
ui = {
icons = {
package_installed = "✓",
package_pending = "➜",
package_uninstalled = "✗",
},
},
})
require("mason-lspconfig").setup({
-- A list of servers to automatically install if they're not already installed
ensure_installed = { "pylsp", "lua_ls", "bashls" },
})
-- Set different settings for different languages' LSP
-- LSP list: https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md
-- How to use setup({}): https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/wiki/Understanding-setup-%7B%7D
-- - the settings table is sent to the LSP
-- - on_attach: a lua callback function to run after LSP attaches to a given buffer
local lspconfig = require("lspconfig")
-- Customized on_attach function
-- See `:help vim.diagnostic.*` for documentation on any of the below functions
local opts = { noremap = true, silent = true }
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>e", vim.diagnostic.open_float, opts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "[d", vim.diagnostic.goto_prev, opts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "]d", vim.diagnostic.goto_next, opts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>q", vim.diagnostic.setloclist, opts)
-- Use an on_attach function to only map the following keys
-- after the language server attaches to the current buffer
local on_attach = function(client, bufnr)
-- Enable completion triggered by <c-x><c-o>
vim.api.nvim_buf_set_option(bufnr, "omnifunc", "v:lua.vim.lsp.omnifunc")
if client.name == "rust_analyzer" then
-- This requires Neovim 0.10 or later
vim.lsp.inlay_hint.enable()
end
-- See `:help vim.lsp.*` for documentation on any of the below functions
local bufopts = { noremap = true, silent = true, buffer = bufnr }
vim.keymap.set("n", "gD", vim.lsp.buf.declaration, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "gd", vim.lsp.buf.definition, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "K", vim.lsp.buf.hover, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "gi", vim.lsp.buf.implementation, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<C-k>", vim.lsp.buf.signature_help, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>wa", vim.lsp.buf.add_workspace_folder, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>wr", vim.lsp.buf.remove_workspace_folder, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>wl", function()
print(vim.inspect(vim.lsp.buf.list_workspace_folders()))
end, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>D", vim.lsp.buf.type_definition, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>rn", vim.lsp.buf.rename, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>ca", vim.lsp.buf.code_action, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "gr", vim.lsp.buf.references, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set("n", "<space>f", function()
vim.lsp.buf.format({
async = true,
-- Only request null-ls for formatting
filter = function(client)
return client.name == "null-ls"
end,
})
end, bufopts)
end
-- How to add a LSP for a specific programming language?
-- 1. Use `:Mason` to install the corresponding LSP.
-- 2. Add the configuration below. The syntax is `lspconfig.<name>.setup(...)`
-- Hint (find <name> here) : https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md
lspconfig.pylsp.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
lspconfig.gopls.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
lspconfig.lua_ls.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
settings = {
Lua = {
runtime = {
-- Tell the language server which version of Lua you're using (most likely LuaJIT in the case of Neovim)
version = "LuaJIT",
},
diagnostics = {
-- Get the language server to recognize the `vim` global
globals = { "vim" },
},
workspace = {
-- Make the server aware of Neovim runtime files
library = vim.api.nvim_get_runtime_file("", true),
},
-- Do not send telemetry data containing a randomized but unique identifier
telemetry = {
enable = false,
},
},
},
})
lspconfig.bashls.setup({})
-- source: https://rust-analyzer.github.io/manual.html#nvim-lsp
lspconfig.rust_analyzer.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
lspconfig.clangd.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
lspconfig.ocamllsp.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
lspconfig.ruby_lsp.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
-- For CMake User (assumption: ./build is the build directory)
-- $ cmake -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1
-- $ ln -s ./build/compile_commands.json .
-- If you don't use any build tool
-- Put compile_commands.json in the root directory of your project
-- The compile_commands.json contains *build flags* (-I ...)
-- see: https://clangd.llvm.org/installation#compile_commandsjson
lspconfig.clangd.setup({
on_attach = on_attach,
})
请注意上述配置中 vim.diagnostic 配置快捷键,这是一个非常有用的功能,当lsp检查出代码错误时会在错误行的开头添加一个 E ,只要将光标移动到错误行,通过快捷键就就能够查看诊断信息:
vim.diagnostic.open_float表示浮动框显示错误信息,这里配置<space>e组合键显示错误诊断浮动框
vim.diagnostic.goto_prev和vim.diagnostic.goto_next分别显示上一个和下一个错误诊断详情
vim.diagnostic.setloclist则是在当前工作窗口切分出一个窗口单独显示错误诊断信息,适合一次性展示多个错误内容的诊断信息j
这里有一个疑惑需要后续解决,就是 <space>e 和 <space>q 这个组合键中的 <space> 在使用中会导致光标移动,需要有一个方法关闭掉交互模式下空格键移动光标的功能(待查)
最后,在
init.lua中加入激活lsp:
~/.config/nvim/lua/init.lua 中激活 lsp.luarequire('options')
require('keymaps')
require('plugins')
require('colorscheme')
require('lsp')
一旦完成上述配置,重启 Nvim ,可以看到 Mason 会安装指定LSP。要跟踪安装,在命令状态输入 :Mason ,此时会看到一个动态安装进度,安装完成后会看到类似如下显示:
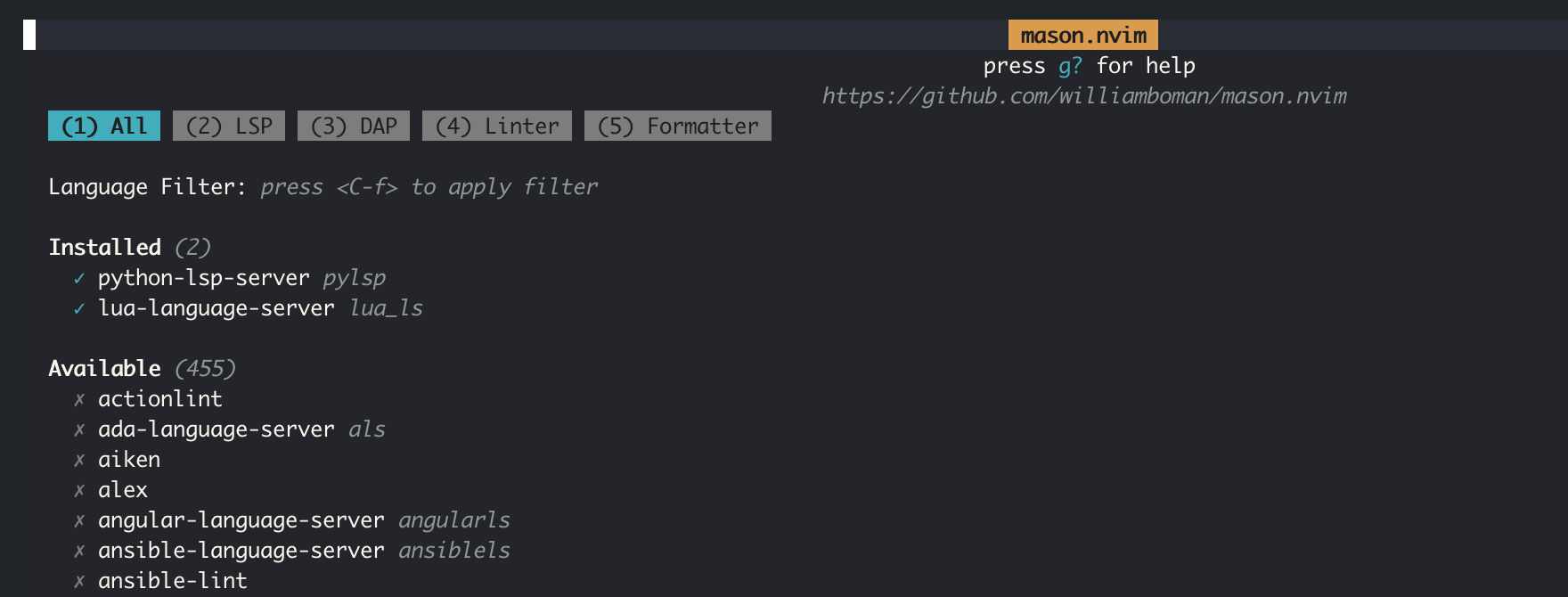
Mason 安装完成LSP的情况
继续探索
参考 Transform Your Neovim into a IDE: A Step-by-Step Guide ,可以完成一个轻量级的IDE,但是这只是一个开始:
获得了一个代码高亮显示、代码自动补全、语法检查等功能,完全采用开源方式构建;但是这仅仅提供了一个案例学习配置,实际生产适配不同语言,需要再深入学习实践
mason.nvim 和 mason-ispconfig.nvim 配置需要针对不同开发语言进行配置和打磨,这有待我后续实践: 我计划把自己学习和使用的语言配置上
这是一个开始,我将继续实践...
参考
Transform Your Neovim into a IDE: A Step-by-Step Guide 我当时没有注意,原来作者是中文/英文双语撰写博客,中文版 从零开始配置 Neovim(Nvim) 阅读更为方便,并且在2024/25年更新了文档,非常清晰易读,推荐阅读原文